The pandemic introduced us to a blended life, mixing real-world living with virtual activities. From working over Zoom to ordering groceries straight to our doorstep, all of us have become accustomed to the digitalization of our routines. And whether you love it or hate it or you’re still trying to understand it, there’s no going back. Digital products and experiences will now continue ranking high among consumers and enterprises’ priorities.
Helping all of this become true are technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR), the combination of which is better known as Extended Reality (XR). Nowadays, these technologies are becoming almost indispensable to anyone seeking to better their digital experiences.
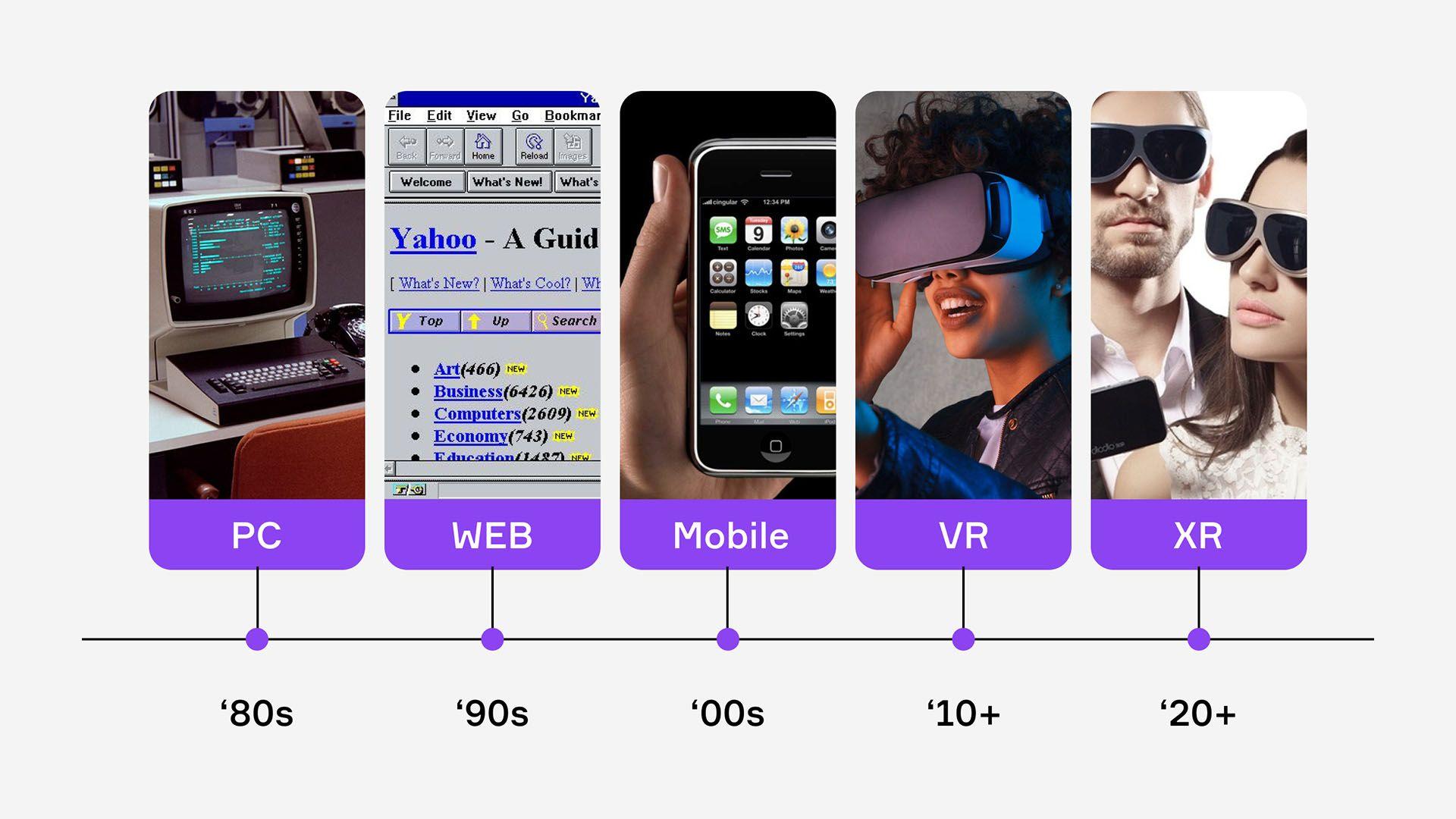
So, today we are taking a closer look at what extended reality is and how does it all work.
What Is Extended Reality
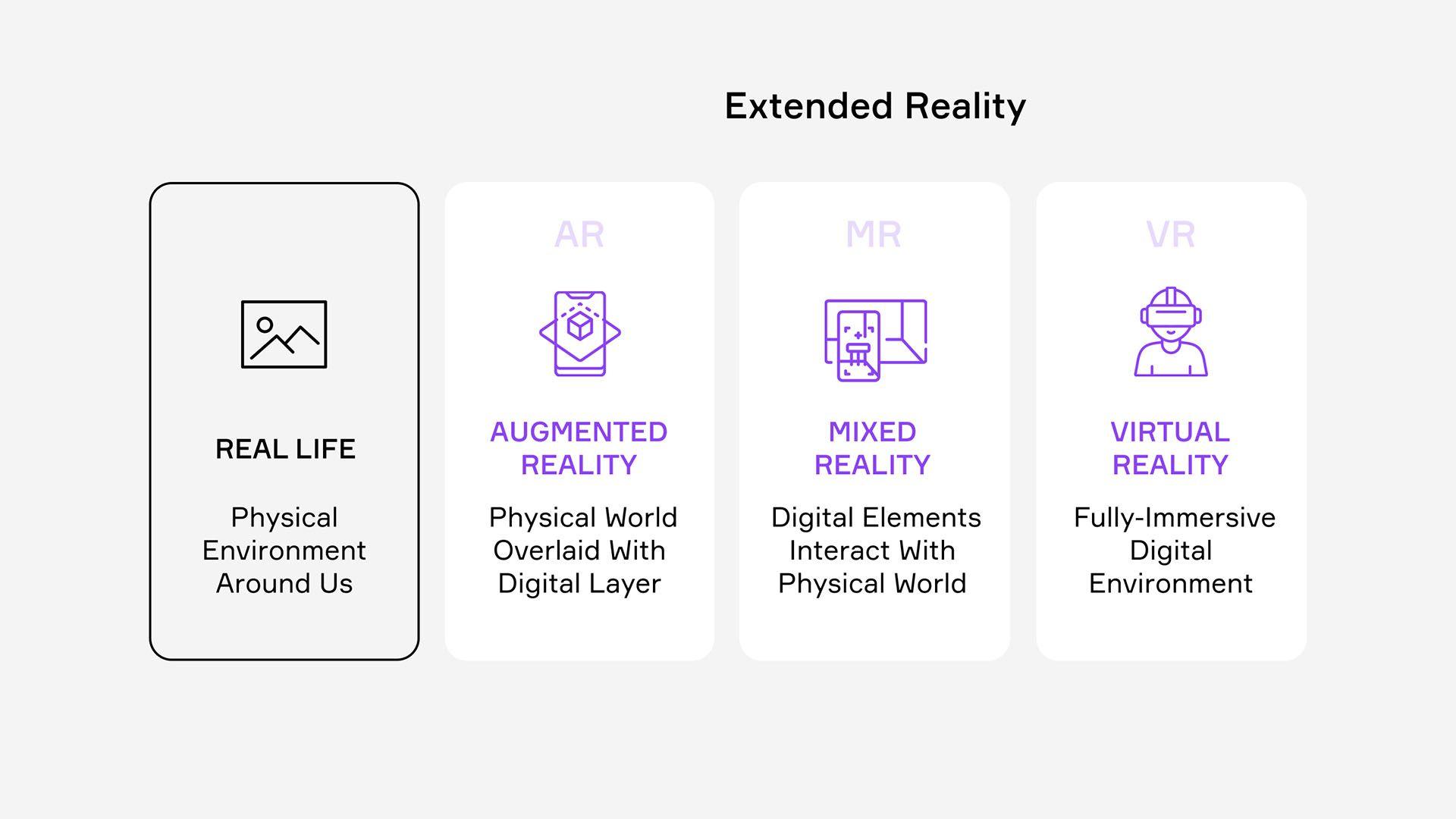
Let’s break down the meaning behind extended reality - and what does the technology stand for. Extended reality (or XR) is an umbrella term for computer-generated environments that merge the physical and virtual worlds or create an entirely virtual experience for users.
XR lies at the intersection of three technologies: virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR). By bringing all of this together, XR can uncover a broad new spectrum of opportunities across real and virtual-based environments.
To have a better understanding of what is extended reality, let’s start by looking at the definition of the three components we mentioned:
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a 3D environment completely generated through computer technology where users can be fully immersed in simulated realities with the help of dedicated headsets, haptic touch and even environmental feedback. If you’re interested in knowing more about VR headsets, here’s a quick guide. In short, virtual reality is capable of generating realistic images and sounds that engage a user’s five senses in a virtual world, much like in real life.
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) does not create a new reality, but rather it overlays images onto the real world. Users can make use of a device like their mobile phone or table to overlay digitally created images and sounds onto their real life environments. Some examples of AR technology at use include Instagram filters, Snapchat’s lenses and Pokémon Go.
Mixed Reality
Mixed Reality (MR) lies somewhere at the intersection of VR and AR. This technology blends real and virtual worlds to create complex environments where physical and digital elements interact in real time.
Extended Reality (XR)
Extended reality extends across VR, AR and MR, as well as all future immersive technologies that enable an extension of reality while blending virtual graphics with real-world elements. Such technologies include, for example, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), 5G network, and others. XR covers the full spectrum of real and virtual environments.
To sum it all up, by using extended reality (XR), people are able to visit virtual environments and engage in experiences in an immersive and interactive way that can realistically match what they can access in the real world. This is the main idea behind the metaverse and why extended reality is crucial to make it all work.
Benefits of Extended Reality
Virtual Reality has some real benefits when it comes to using the technology to enhance certain experiences, including:
Improved Learning
XR creates a safe learning space in schools and universities, where learners and educators can explore experiential learning methods. In addition, extended reality is an opportunity to improve learning rates as research shows that learners in conventional settings tend to forget some 70% of the content they’ve been exposed to within 24 hours and nearly 90% in a month. On the other hand, studies around extended reality show that when the technology is employed in classrooms, students have demonstrated improved comprehension and retention. XR is also a valuable too in engaging students who face cognitive challenges or those who respond better to different learning platforms.
Effective Training and Development
Extended reality technology is becoming a common platform for educational institutions as well as companies looking to help staff develop new skills in a safe environment. Here, there are many advantages that can be highlighted, including knowledge retention, lower operational costs, and increased engagement.
Better Customer Experience
With XR, brands can reach new customers and offer innovative ways of letting them engage with products and services. For example, clients can try out clothing or watch demonstrations that can result in better experiences when compared to real world offerings. Customer support can also greatly benefit from adopting XR tools.
Enabling Remote Work
Distance work became a norm during the Covid-19 pandemic and the trend appears to see an adoption even after its end. VR, AR and MR allow workers to better interact with their peers and collaborate in more effective ways when compared to 2D platforms like Zoom or Skype. A virtual environment opens the doors to more possibilities that can ultimately translate into better performance for workers and companies.
Enhanced Entertainment Experiences
Virtual reality gatherings are also becoming a trend across the entertainment industry, with several artists choosing to hold their concerts online. In 2021, we also saw a roster of performers dabbling in the metaverse. Moving forward, we can expect the industry to boom as concerts, conferences, meet-ups and a range of events move to all-virtual environments. This trend will be particularly prevalent in the metaverse, as is the case of Sensorium Galaxy - a metaverse dedicated to entertainment offerings across music, dance, and more.
Challenges In Adopting Extended Reality
While there are many benefits to adopting XR, there are still some challenges to overcome until it becomes mainstream:
Cost:
Given that XR is a relatively new form of technology, there may be higher upfront development and equipment costs compared to other traditional technologies. Developing compelling content for XR users, for example, requires time and the backing of developers committed to the technology, while users have to fork out for interfaces like VR headsets and motion sensors.
User experience:
Experts say that one day users might be able to use VR headsets for 10 or more hours per day. However, for now, users are still experiencing some health complaints from using such headsets for shorter periods of time, including motion sickness, eye strain and headaches.
Hardware issues:
The interfaces needed to access extended technology, devices and interfaces, still face a wide host of challenges when displaying visuals accurately. Improvements can be expected as adjacent technologies like 5G and edge computing will also see advancements, helping XR become increasingly more complex.
Skepticism:
The technology is yet to win over large audiences as many consumers are yet to understand the benefits and various applications of the technology. Additionally, there’s a general lack of clarity regarding issues like data privacy and security, which may weigh on the mind of consumers when deciding whether or not to experiment with extended reality technology.
Use Cases of Extended Reality
Organizations have begun understanding the potential of using digital technology to create or extend valuable experiences.
Current use cases have started highlighting the potential of XR across several industries and spheres:
Entertainment: The immersive experiences enabled by XR open an opportunity for music, sports and other entertainment events to become even more engaging and compelling, while fans can have access to an endless catalog of events from the comfort of their home, with a VR headset.
Marketing: Virtual worlds are a new frontier for marketing and advertising, where brands can engage with new consumers and offer novel ways of presenting and interacting with virtual products.

Real Estate: Brokers and property owners can optimize real estate services by letting potential clients and tenants tour properties in a virtual format. By the same token, interior designers and architects can leverage XR for layouts, designs, and construction plans.
Healthcare: XR technology can offer better analysis for professionals of the medical industry, offering training possibilities for surgeries, diagnosis and treatments.
Tourism: Potential travelers can have a sneak peak at locations and infrastructures like landmarks and hotels before committing to buying tickets to the preferred destination.
Industry Manufacturing: In this sector, extended reality has the potential to help companies improve safety measures, develop effective training and diagnose real-time issues.
Remote Work: By using extended reality tech, companies can allow their workers to work virtually, attend meetings, collaborate and access information, no matter their physical location.
Examples of Extended Reality Applications
VR, AR and MR have the potential to transform the way we interact with day-to-day aspects, across a wide range of industries. And combined, as XR technology, this will be equally transformative for both consumers and enterprises. According to a recent survey, seventy-one percent (71%) of companies had planned to increase their use of extended reality technologies in 2021, a number that is likely to see a rise in 2022.
Here are some examples of companies using extended reality:
The German automaker has deployed extended reality technology in self-driving simulations. In virtual worlds built specifically for the purpose, BMW can test and simulate any scenario and accelerate autonomous vehicle development.
As a way of enhancing vehicle design visualization, Honda has resorted to XR to create exceptional interactive presentations of their car designs in a single day.
Consultancy firm Accenture has made a massive investment in XR tools, using them for training staff as well as helping clients imagine, create and deliver innovative XR experiences at enterprise scale.
Consumer electronics maker HTC, known for its HTC Vive VR headsets, has a wide range of XR enterprise and consumer options across five different apps - Vive Sessions, Vive Sync, Vive Campus, Vive Social (provided by VRChat) and Vive Museum.
Bottom Line
While XR is yet to be a reality that can be permanently present in our everyday lives, it is already setting the future evolution of the world reflected in advancements like the metaverse. XR poses a valuable opportunity for segments like entertainment, marketing, sports, tourism, education, and much more. As technology continues evolving, we will likely see extended reality becoming indispensable to us all.




